What Does Atopic Dermatitis Look Like when it Needs Treatment?
What Does Atopic Dermatitis Look Like when it Needs Treatment?
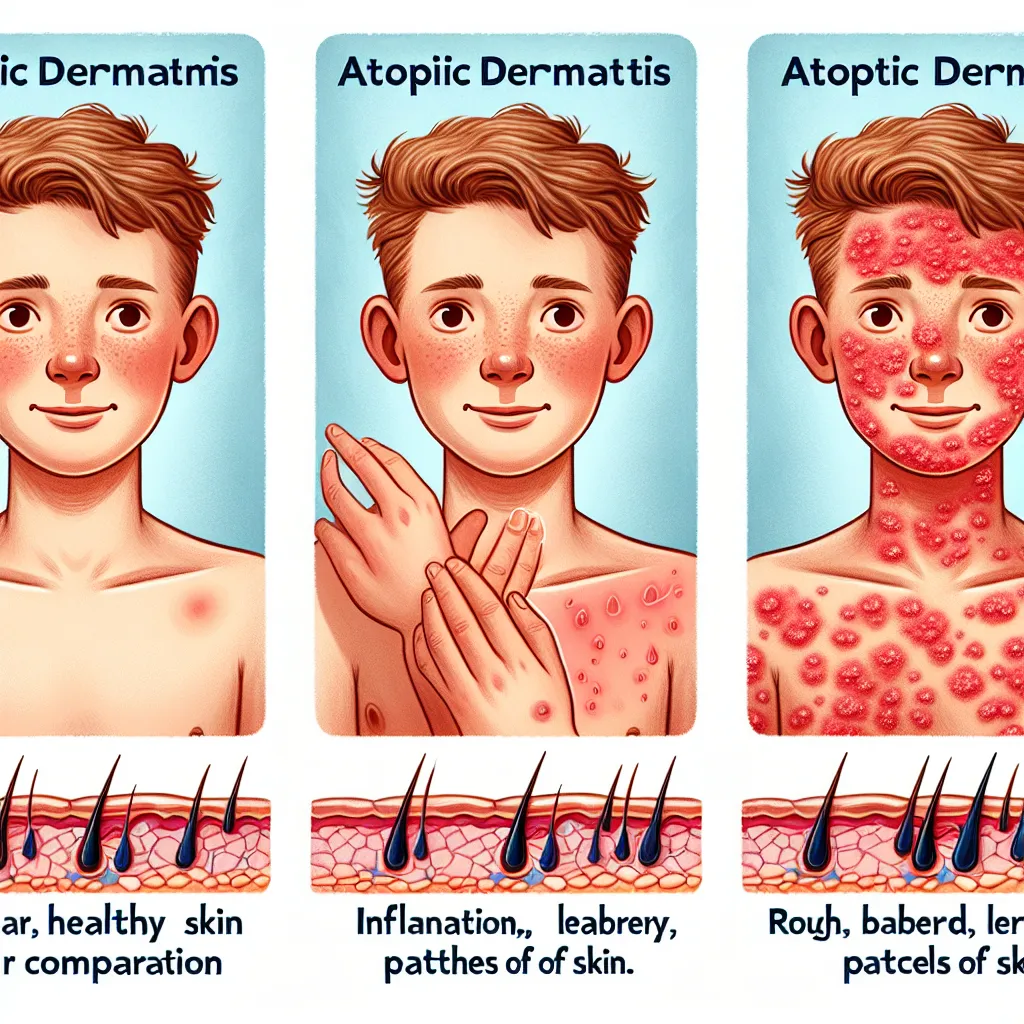
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by itchy, inflamed, and dry skin. While the symptoms may vary from person to person, it is crucial to recognize when atopic dermatitis requires treatment to manage the condition effectively. In this article, we will discuss the visible signs of atopic dermatitis and when it is essential to seek medical assistance.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a form of eczema that is often associated with other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever. It is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects both children and adults. The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
The most common symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
- Intense itching
- Red or brownish-gray patches on the skin
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
- Small raised bumps that may leak fluid and crust over when scratched
- Thickened, leathery skin
- Sensitive and swollen skin from scratching
Identifying When Treatment is Needed
While atopic dermatitis can be managed with self-care measures and lifestyle changes, there are instances when medical intervention becomes necessary. It is important to recognize when the condition requires treatment to prevent worsening symptoms and improve the overall quality of life.
1. Severe Itching:
Atopic dermatitis is known for causing intense itching, which can be extremely uncomfortable and disruptive. If the itching becomes severe and starts affecting your daily activities, it is a sign that you may need treatment. Scratching excessively can further damage the skin, leading to infections and other complications.
2. Persistent Symptoms:
If your symptoms persist despite using over-the-counter treatments and home remedies, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist. Persistent redness, dryness, and inflammation may indicate that your atopic dermatitis requires prescription medications or specialized treatments.
3. Sleep Disturbance:
Atopic dermatitis can significantly disrupt sleep due to constant itching and discomfort. If your sleep pattern is consistently disturbed, resulting in fatigue and decreased productivity during the day, seeking medical attention is crucial. A dermatologist can help identify the underlying causes and provide suitable treatment options to improve your sleep quality.
4. Infection:
When the skin barrier is compromised due to atopic dermatitis, it becomes more susceptible to bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. If you notice signs of infection such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, pus-filled blisters, or fever, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Infections require prompt treatment with antibiotics or antifungal medications to prevent further complications.
5. Emotional Impact:
Living with atopic dermatitis can take a toll on one’s emotional well-being. The constant discomfort, visible skin changes, and social stigma associated with the condition can lead to feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, and depression. If your atopic dermatitis is affecting your mental health and overall quality of life, it is essential to reach out to a healthcare professional who can provide emotional support and recommend appropriate treatments.
Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis
When atopic dermatitis requires treatment, there are various options available depending on the severity and individual needs. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Here are some common treatment approaches:
1. Topical Corticosteroids:
Corticosteroid creams or ointments are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching. They are available in different strengths and should be used as directed by a healthcare professional.
2. Moisturizers:
Regularly applying moisturizers can help hydrate the skin and prevent dryness, which is a common trigger for atopic dermatitis flare-ups. Look for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic moisturizers that are suitable for sensitive skin.
3. Immunosuppressants:
For severe cases of atopic dermatitis that do not respond to other treatments, immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. These medications require close monitoring and should only be used under the supervision of a dermatologist.
4. Phototherapy:
Phototherapy involves exposing the affected skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet light. It can help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in some individuals with atopic dermatitis. However, this treatment option should be carefully administered and monitored by a healthcare professional.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage atopic dermatitis. These include avoiding triggers such as harsh soaps, fragrances, and allergens, wearing soft and breathable fabrics, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, and stress management techniques.
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life if left untreated. Recognizing the signs that indicate the need for treatment is crucial to effectively manage the condition and prevent complications. If you experience severe itching, persistent symptoms, sleep disturbances, signs of infection, or emotional distress, it is important to seek medical assistance from a dermatologist. With proper diagnosis and personalized treatment options, individuals with atopic dermatitis can find relief and improve their skin health.
